Learn about Types of Radiography Technology. These services include X-rays, digital radiography, fluoroscopy, and industrial radiography, all of which provide accurate imaging and analysis for medical diagnostic, security, and manufacturing purposes.
Introduction
Using X-rays on one’s body, radiography technology produces these image assessments of internal body structures in medicine. Thus images of bones and organs necessitated for diseases like infection, fractures, and overall body disorders are at play in the medical industry.
The control of all types of radiologic equipment used to obtain meaningful radiographic images while minimizing the risk of exposure is the responsibility assumed by radiographers for themselves in the above definition. Therefore, radiography technology occupies a very important place in the diagnosis and treatment of 21st-century health care.
Types of Radiography Technology
1. X-Ray Radiography
Flat-panel radiography uses a controllable amount of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of high detail. The method is, therefore, widely employed in medical diagnostics for the detection of fractures, infections, and tumors.
2. Computed Radiography (CR)
With computed radiography, images are taken on reusable imaging plates that store the information imparted by the radiation and convert it into a digital form for further analysis, resulting in an image of fine quality. CR, however, is slower than film X-ray but de faster and more convenient than film.
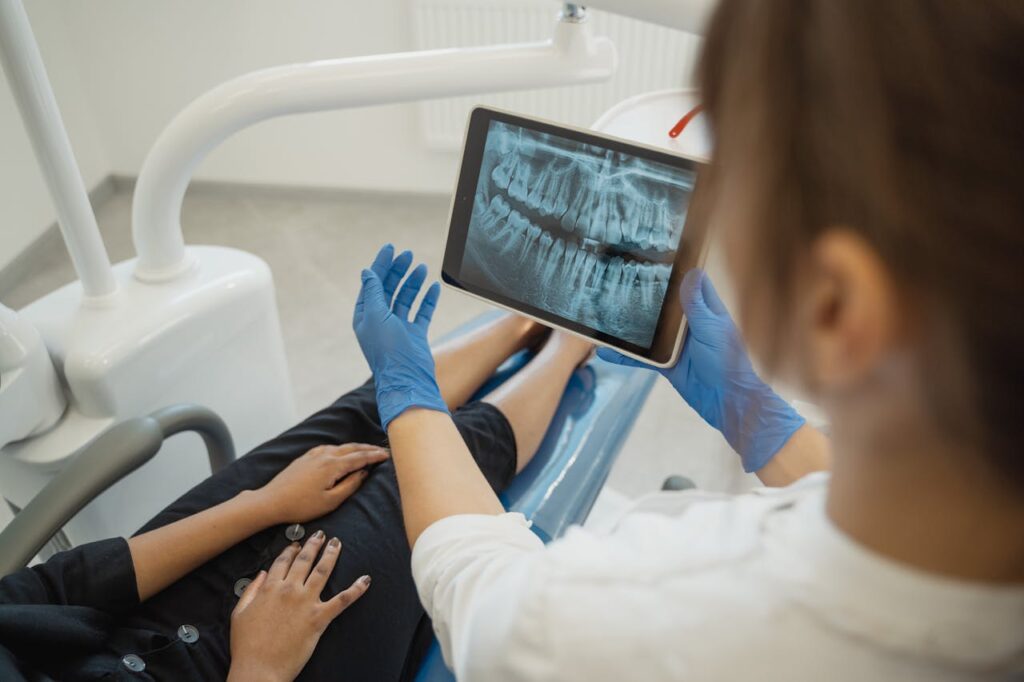
3. Digital Radiography (DR)
Digital Radiography is an advanced method of imaging that acquires images using digital sensors instead of film. It provides immediate imaging with superior clarity, contrast, and data storage. Because of the speed and accuracy, DR is the most favored system for both medical and industrial applications.
4. Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy, often defined as the observation of moving pictures in real-time under the constant X-ray exposure of a patient, is relevant to multiple applications such as angiography, catheter placements, and gastrointestinal tract studies. It allows doctors to see the instant motion of internal structures.
5. Industrial Radiography
Radiography is the process of inspecting welds, pipelines, and machinery for failure by assuring structural integrity and proper functioning in the fields of construction, manufacturing, and aerospace. High-energy X-rays and gamma rays penetrate metals and composites to show cracks and voids in an image.
Applications of Radiography Technology
1. Medical Diagnostics
Radiology is one of the basic tools in the purview of modern medicine. It is instrumental in identifying: injuries, infections, tumors, pneumonia, and diseases of the cardiovascular system. Advanced CT scans and mammography radiographers give an extremely fine detail that allows for test results to be interpreted accurately.
2. Industrial Testing
Radiography is important for the safety and quality of manufactured products. Its purpose is to find defects in a material, weld, or equipment that are hidden from view and which could eventually destroy the integrity of the item. This non-destructive testing comes in handy when used in the construction, auto, and naval industries.
3. Aerospace and Manufacturing
Radiography benefits the aerospace industry in that it is applied to detect internal cracks and structural weaknesses in elements of aircraft components so that failures do not occur. Manufacturers brush up on radiography in composite materials testing to ensure product reliability.
4. Security and Defense
In airport security, radiography is applied in baggage scanning to find any weapons or explosives concealed within. Radiographic technology improves surveillance and threat detection capabilities in border security and military operations.
The Evolution of Radiography Technology
The development of the field of radiography took a giant leap forward since the day X-rays were discovered by Wilhelm Roentgen in 1895. The first few years of X-ray imaging were very crude and lasted a long time in exposure.
Yet digital radiography, computed tomography, and fluoroscopy continued evolving to become precise. Artificial Intelligence and machine learning today are making forays into radiographic interpretation, diminishing human errors and enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
Core Principles of Radiographic Imaging
Radiographic imaging underlines the ability of X-rays to penetrate the body and act courageously with tissues of differing densities.
Dense structures like bone absorb higher amounts of radiation and thus appear whitish on an x-ray film while soft tissues absorb relatively lesser amounts and thus appear as shades of gray.
Modern techniques involve injecting certain contrast agents in a selected manner to detail organs and vascular structures, allowing for much sharper evaluations.
Key Modalities in Radiography Technology
1. Conventional X-ray Imaging
X-rays of the conventional type are the most widely indicated radiography. For example, they may be used to diagnose a fracture, lung infection, or even some dental conditions. More often than not, digital radiography will overshadow film-based X-rays because of the time-saving and improved quality of images.
2. Computed Tomography (CT)
Sounds like fun! CT or Computed Tomography-test scans use a technique to get cross-sectional images of the body through multiple X-ray images taken from a variety of angles. Here allows reconstruction in three realization of organ detail as well as focusing closer examination of the tumors and structures in blood vessels.
3. Fluoroscopy
Dynamic fluoroscopy allows real-time moving images of the digestive tract or to see the flow of blood through the arteries. It is an imaging process utilized by physicians to assist in minimally invasive procedures such as catheter insertions and angiography.
4. Mammography
Mammography is defined as an X-ray technique for the diagnosis of breast cancer. With low-x-ray dosage, it provides intricate images of the tissue and allows cancer to be diagnosed earlier.
5. Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA)
Key DEXA application is a measurement of bone mineral density, leading to the diagnosis of osteoporosis. While X-rays at different energy levels are indirectly used to differentiate bone from soft tissues, DEXA uses dual-energy sources at different levels.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Radiography
The roles of artificial intelligence in transforming radiography technologies. Machine learning algorithms can analyze the diagnostic images in radiography to search for anomalies aiding diagnosis and preventing misinterpretations. The AI software indicates the possible position of a fracture, possible tumors, and infected regions, thus improving the efficiency of diagnosis against the human eye.
Specialized Career Paths in Radiography Technology
Radiography technology offers various career opportunities other than the so-called traditional diagnostic imaging. Here are some atypical career options:
1. Interventional Radiography Specialist
Fluoroscopy-assisted professionals perform their best to assist in minimally invasive procedures such as stenting and biopsy. They work most accurately with the hands of surgeons and cardiologists.
2. Forensic Radiographer
Forensic radiographers work with police departments for the identification of skeletal human remains and any particular person regarded as a fatality. Forensic radiographic technology is a major adjunct to forensic examination helpful in the identification of foreign bodies, trauma, or injuries.
3. Veterinary Radiographer
Veterinary radiographers perform imaging of animals to provide an accurate diagnosis of any diseases and/or injuries. This area requires knowledge of the anatomy of the different species and the imaging modifications applicable to the species under examination.
4. Industrial Radiographer
Industrial radiography goes beyond its use in the medical field. Such experts employ radiation to check the material’s integrity in industries like aerospace, construction, and manufacturing. They assist in revealing weaknesses in bridge structures, planes, and pipes.
Ethical Considerations in Radiography
The fact that radiography technology refers under a banner of ethical concerns such as radiation exposure, patient privacy, etc., brings into being some key ethical issues.
1. Radiation Safety and Protection
Radiographic imaging is non-invasive, but there are risks associated with exradiation exposureThere are certain procedures prescribed for safe practice involving radiologic technologists: lead aprons, minimizing exposure time, and proper shielding for themselves and their patients.
2. Informed Consent
Patients should be duly informed about the risks as well as the benefits of a radiographic procedure. Informed consent is critical, especially in cases where contrast-based imaging studies may lead to allergic reactions and other adverse effects.
3. Data Security and Confidentiality
Digital radiography has made the need for privacy paramount in patient data. Radiologic images carry sensitive medical information and should be kept and transmitted so that they are not compromised by unwanted access.
Future Trends in Radiography Technology
Technological advancements in radiography continue to advance and dictate the discipline’s future. Here are some of the major trends anticipated in the future:
1. Portable and Mobile Imaging
The introduction of mobile X-ray and CT scanners enables imaging to be performed right at the patient’s side, thereby increasing accessibility to emergency and far-off places.
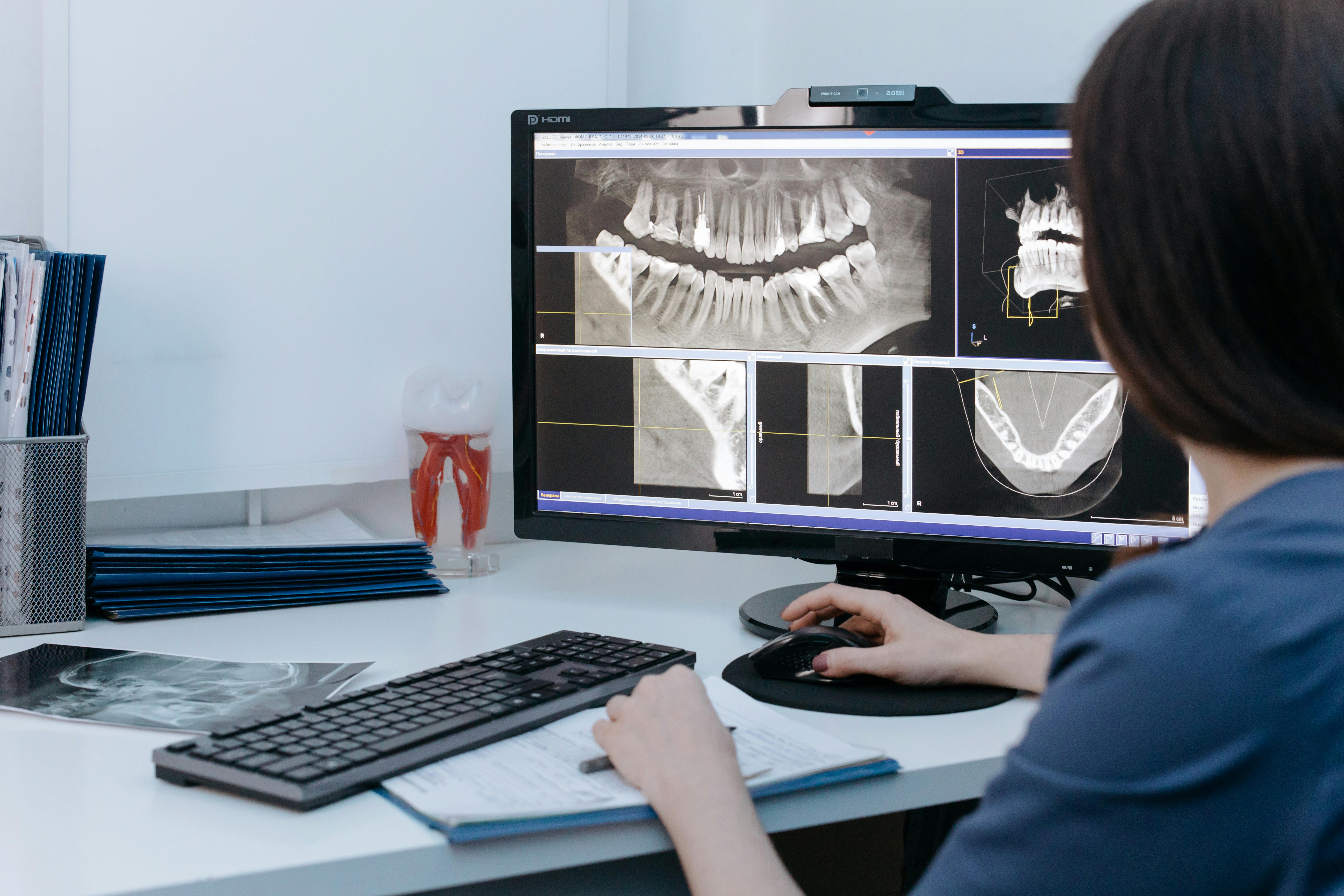
2. Radiomics and Personalized Medicine
Radiomics activity includes the quantitative extraction of data from radiographic imaging to predict how a disease evolves and how it responds to treatment. It is thus aimed toward personalized medicine, where imaging biomarkers will help predict treatments.
3. Hybrid Imaging Technologies
These methods combine to develop hybrid modalities of imaging; for example, PET-CT as well as SPECT-CT. All these technologies help in gathering a complete diagnosis for a patient. They also help diagnose diseases or plan the course of treatment.
Conclusion
Radiographic technology is surely one of the bases of current diagnosis and quality assurance. These span from medical imaging to industrial testing to security screening. Technology progresses, radiography moves on with advancements in fast, safe, and more precise imaging solutions; even now, radiography is an essential modality of imaging for detecting health-related problems or structural integrity.






